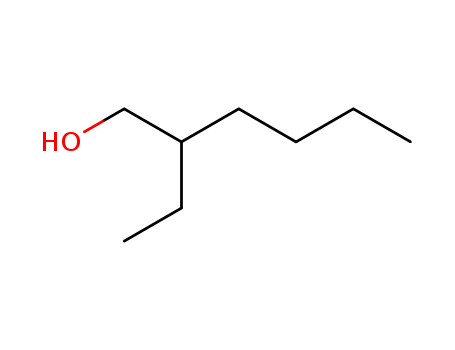
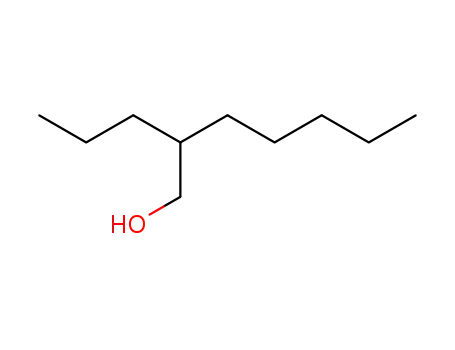
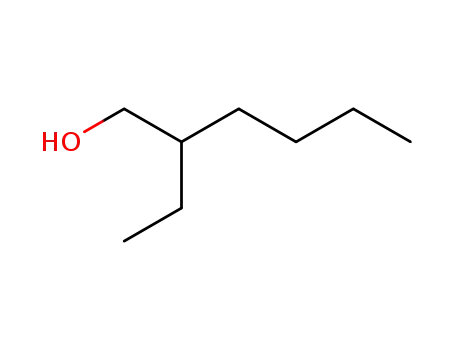
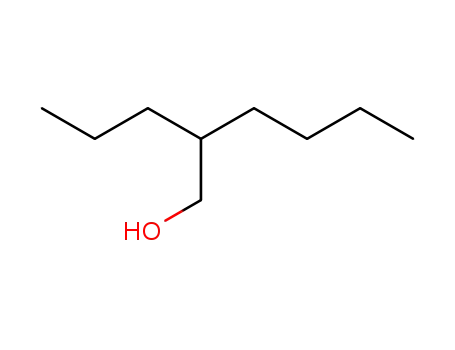
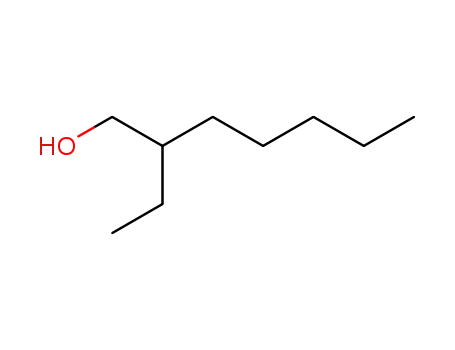
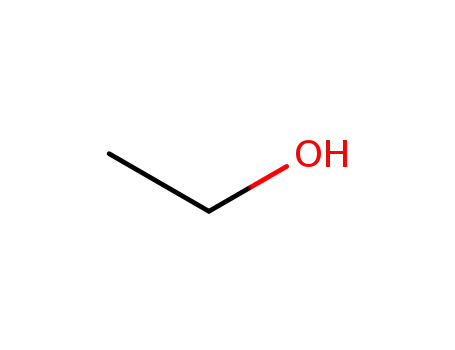
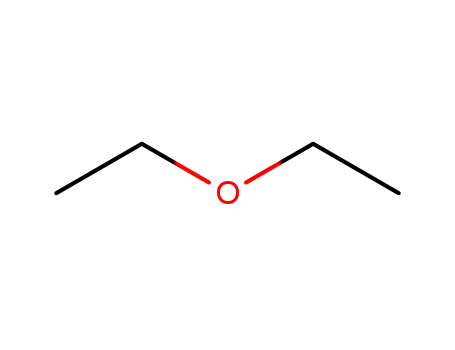
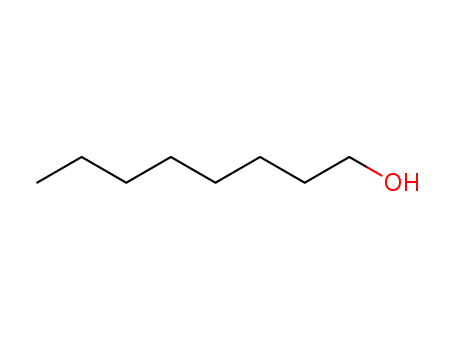
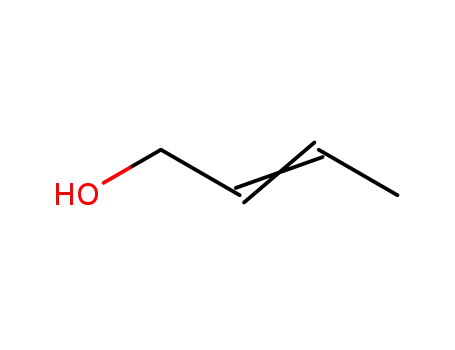
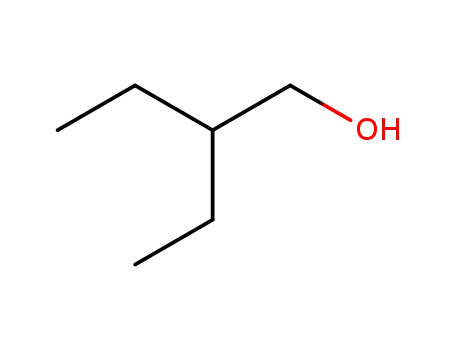
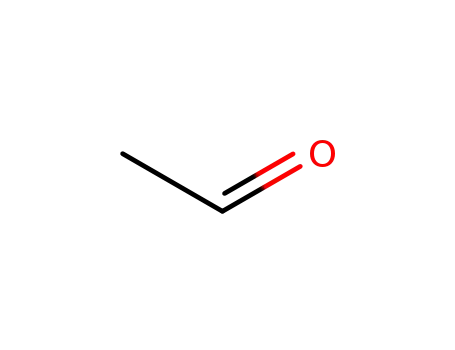
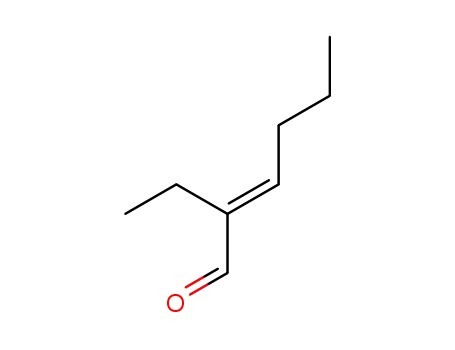
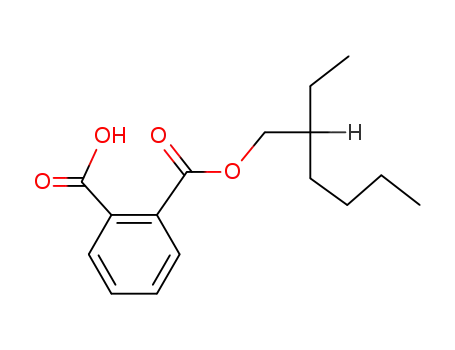
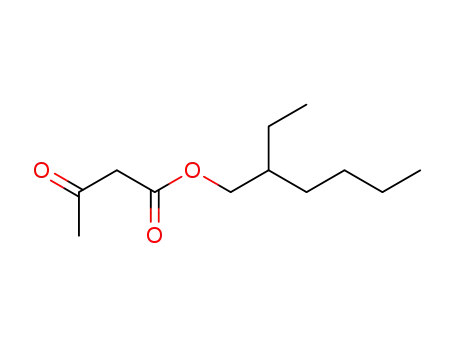
Preparation and properties of lubricant basestocks from epoxidized soybean oil and 2-ethylhexanol
Hong-Sik Hwang, Atanu Adhvaryu, Sevim Z. Erhan
, Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, Volume80, Issue8 August 2003 Pages 811-815
Pour points of the products were observed as lows as −21 and −30°C without and with 1% of pour point depressant, respectively. When the hydroxy groups in the products were esterified with an acid anhydride, lower pour points were observed. Pour point depression of the product by adding PAO has been tested. Oxidative stability of the product was examined using pressurized DSC and compared with those of synthetic lubricant basestocks, PAO, and a synthetic ester.
Journal of Surfactants and Detergents Original Article Open Access
Wiesław Hreczuch, Karolina Dąbrowska, Arkadiusz Chruściel, Agata Sznajdrowska, Katarzyna Materna
, Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, Volume19, Issue1 January 2016 Pages 155-164
The synthesis and basic properties of 2-ethylhexanol based innovative nonionic surfactants are described in this paper. 2-Ethylhexanol as an available and relatively inexpensive raw material was used as the hydrophobe source modified by propoxylation and followed by polyethoxylation.
Non-Oxidative Dehydrogenation Pathways for the Conversion of C2-C4 Alcohols to Carbonyl Compounds
Shylesh, Sankaranarayanapillai,Kim, Daeyoup,Ho, Christopher R.,Johnson, Gregory R.,Wu, Jason,Bell, Alexis T.
, p. 3959 - 3962 (2015)
Gold nanoparticles (NPs) supported on hy...